Augmented Reality (AR) technology has transcended the boundaries of science fiction to become a daily utility, transforming how we interact with the world around us. At its core, AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, but it’s the key features of AR apps that turn this innovative concept into an immersive experience. These features not only define the user experience but also highlight the potential of augmented reality in various applications.
Real-time Interaction – Augmented Reality

One of the most compelling features of AR is its ability to interact with the environment in real time. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates a completely digital environment, AR uses the existing environment and overlays new information on top of it. This interaction is seamless, with AR apps capable of recognizing and mapping real-world objects to provide contextually relevant digital experiences. For instance, in educational apps, students can point their devices at a textbook illustration to see a 3D model emerge, providing a dynamic learning experience.
3D Experiences

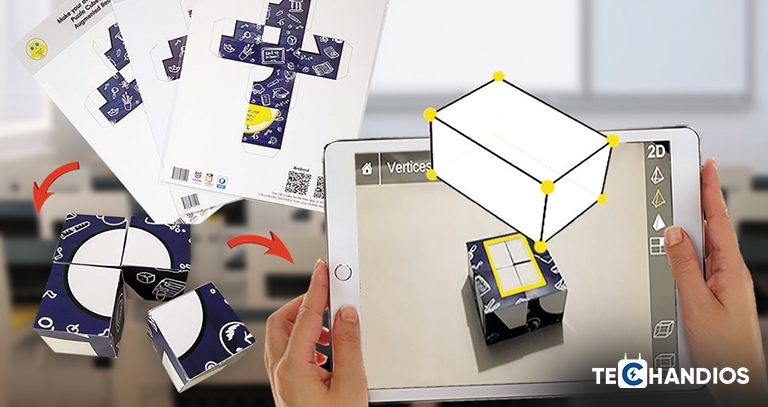
The ability to create 3D models that users can view and interact with from all angles sets AR apart. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries like retail, where customers can visualize how a piece of furniture would look in their living space before making a purchase. IKEA Place is a stellar example, allowing users to place true-to-scale 3D models of furniture in their homes through their smartphone screens, revolutionizing the shopping experience.
Integration with Mobile Devices and Wearables

The widespread adoption of Augmented Reality (AR) has been largely driven by its integration with mobile devices and wearables. Smartphones, with their advanced cameras and sensors, serve as the perfect platform for Augmented Reality (AR) apps, making the technology accessible to a vast audience. Furthermore, wearables like AR glasses enhance the hands-free experience, enabling users to receive navigational cues or translated text in real time as they explore a foreign city, blending digital content with the real world effortlessly.
User Interface and Usability Considerations

The success of an AR app heavily relies on its user interface (UI) and usability. Augmented Reality apps must be intuitive, allowing users to navigate and interact with digital elements naturally. Designing for AR requires a deep understanding of spatial interaction, ensuring that digital objects behave in ways that are consistent with the real world. The UI should be minimalistic, avoiding overcrowding the user’s field of view, while providing enough context for the AR experience to be meaningful and engaging.
Popular AR Apps and Their Uses

Highlighting the versatility of AR, numerous apps have emerged across different sectors, showcasing the technology’s broad appeal:
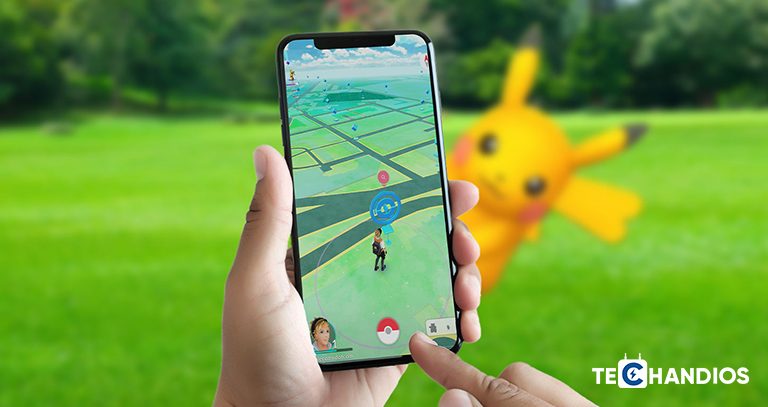
- Gaming: Pokémon Go took the world by storm by allowing players to catch virtual creatures in real-world locations, blending physical activity with digital gaming.

- Education: Apps like Anatomy 4D change how students learn about the human body, offering interactive, 3D views of organs and systems.
- Retail and Fashion: Warby Parker’s app uses AR to let customers try on glasses virtually, making online shopping more personal and accurate.

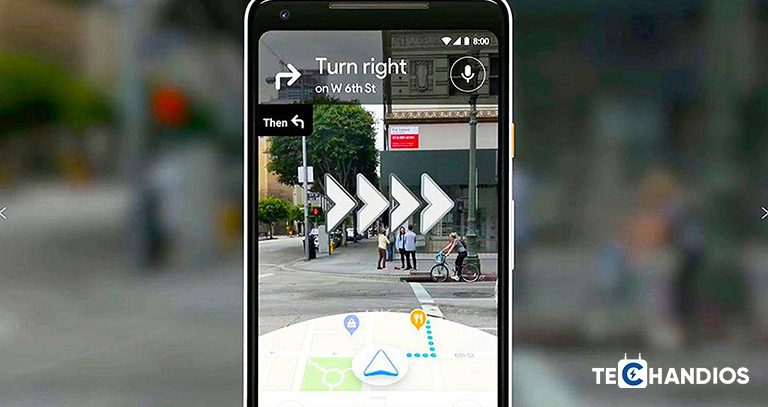
- Travel and Navigation: Google Maps AR walking directions provide users with real-time, overlaid navigational cues on their phone screen, simplifying urban navigation.
Conclusion
The key features of AR apps‚Äîreal-time interaction, 3D experiences, integration with mobile devices and wearables, and thoughtful UI design‚Äîunderscore the technology’s transformative potential. As AR continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more innovative applications that will further blur the lines between the digital and physical worlds, enhancing our daily lives in myriad ways. The future of AR is bright, promising a world where digital information enhances our reality, making it richer, more interactive, and infinitely more engaging.